Connecting to Tor¶
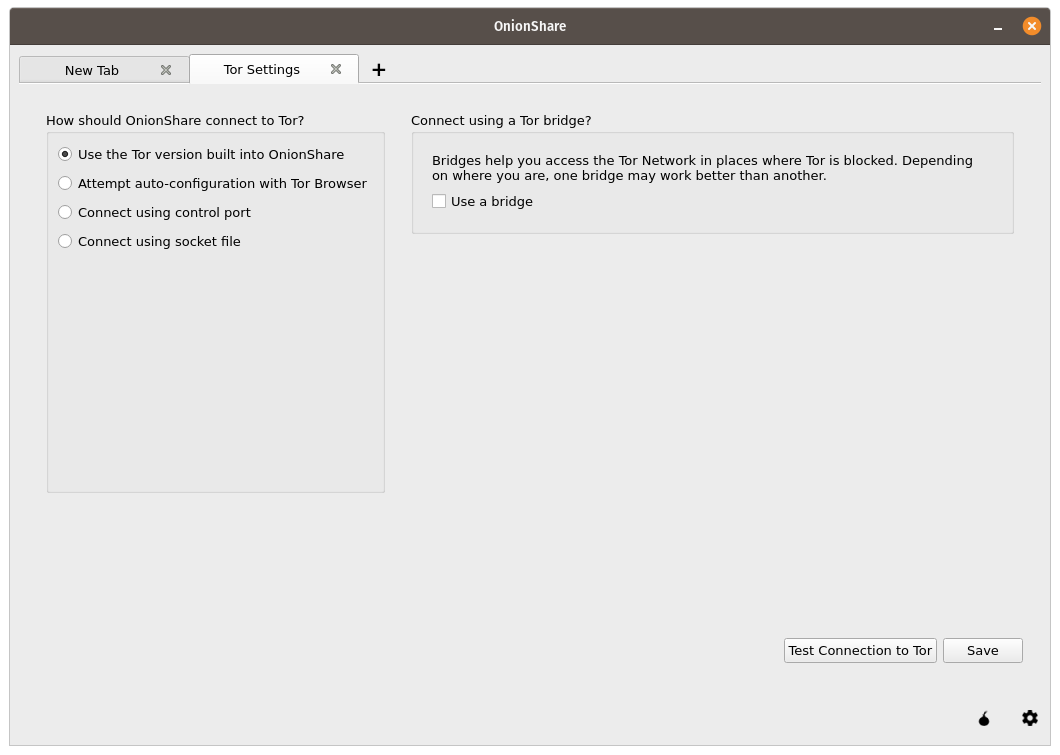
Pick a way to connect OnionShare to Tor by clicking the Tor onion icon in the bottom right of the OnionShare window to open the Tor Settings tab.
Getting Around Censorship¶
If your access to the internet is censored, you can configure OnionShare to connect to the Tor network using Tor bridges. If OnionShare connects to Tor without one, you don’t need to use a bridge.
To use a bridge, open the Tor Settings tab. You must select “Use the Tor version built into OnionShare” and check the “Use a bridge” checkbox.
Try using a built-in bridge first. Using obfs4 or snowflake bridges is recommended over using meek-azure.
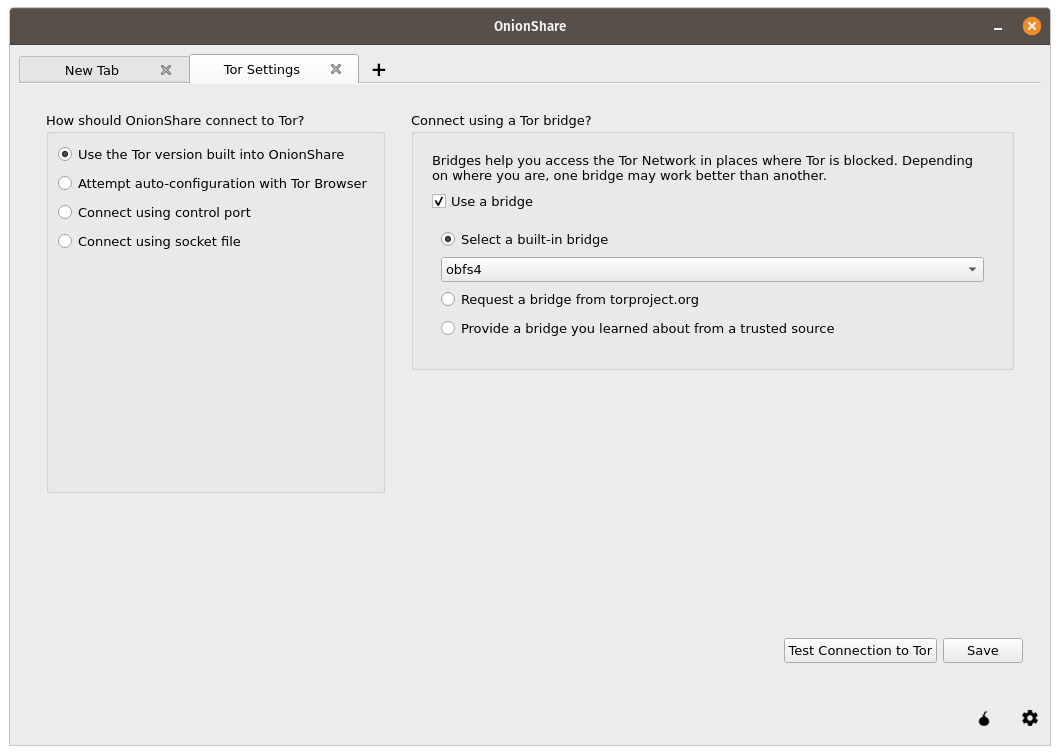
If using a built-in bridge doesn’t work, you can request a bridge from torproject.org. You will have to solve a CAPTCHA in order to request a bridge. (This makes it more difficult for governments or ISPs to block access to Tor bridges.)
You also have the option of using a bridge that you learned about from a trusted source.
Attempt auto-configuration with Tor Browser¶
If you have downloaded the Tor Browser and don’t want two tor processes running, you can use the tor process from the Tor Browser.
Keep in mind you need to keep Tor Browser open in the background while you’re using OnionShare for this to work.
Using a system tor in Windows¶
This is fairly advanced. You’ll need to know how edit plaintext files and do stuff as an administrator.
Download the Tor Windows Expert Bundle from.
Extract the compressed file and copy the extracted folder to C:\Program Files (x86)\
Rename the extracted folder with Data and Tor in it to tor-win32.
Make up a control port password.
(Using 7 words in a sequence like comprised stumble rummage work avenging construct volatile is a good idea for a password.)
Now open a command prompt (cmd) as an administrator, and use tor.exe --hash-password to generate a hash of your password. For example:
cd "C:\Program Files (x86)\tor-win32\Tor"
tor.exe --hash-password "comprised stumble rummage work avenging construct volatile"
The hashed password output is displayed after some warnings (which you can ignore). In the case of the above example, it is 16:00322E903D96DE986058BB9ABDA91E010D7A863768635AC38E213FDBEF.
Now create a new text file at C:\Program Files (x86)\tor-win32\torrc and put your hashed password output in it, replacing the HashedControlPassword with the one you just generated:
ControlPort 9051
HashedControlPassword (the hash you generate from the password you picked above)
In your administrator command prompt, install tor as a service using the appropriate torrc file you just created (as described in https://2019.www.torproject.org/docs/faq.html.en#NTService). Like this:
tor.exe --service install -options -f "C:\Program Files (x86)\tor-win32\torrc"
You are now running a system tor process in Windows!
Open OnionShare and click the “⚙” icon in it.
Under “How should OnionShare connect to Tor?” choose “Connect using control port”, and set
“Control port” to 127.0.0.1 and
“Port” to 9051.
Under “Tor authentication settings” choose “Password” and set the password to the control port password you picked above.
Click the “Test Connection to Tor” button.
If all goes well, you should see “Connected to the Tor controller”.
Using a system tor in macOS¶
First, install Homebrew if you don’t already have it, and then install Tor:
brew install tor
Now configure Tor to allow connections from OnionShare:
mkdir -p /usr/local/var/run/tor
chmod 700 /usr/local/var/run/tor
echo 'SOCKSPort 9050' >> /usr/local/etc/tor/torrc
echo 'ControlPort unix:"/usr/local/var/run/tor/control.socket"' >> /usr/local/etc/tor/torrc
And start the system Tor service:
brew services start tor
Open OnionShare and click the “⚙” icon in it.
Under “How should OnionShare connect to Tor?” choose “Connect using socket file”, and
set the socket file to be /usr/local/var/run/tor/control.socket.
Under “Tor authentication settings” choose “No authentication, or cookie authentication”.
Click the “Test Connection to Tor” button.
If all goes well, you should see “Connected to the Tor controller”.
Using a system tor in Linux¶
First, install the tor package. If you’re using Debian, Ubuntu, or a similar Linux distro, It is recommended to use the Tor Project’s official repository.
Next, add your user to the group that runs the tor process (in the case of Debian and Ubuntu, debian-tor) and configure OnionShare to connect to your system tor’s control socket file.
Add your user to the debian-tor group by running this command (replace username with your actual username):
sudo usermod -a -G debian-tor username
Reboot your computer.
After it boots up again, open OnionShare and click the “⚙” icon in it.
Under “How should OnionShare connect to Tor?” choose “Connect using socket file”.
Set the socket file to be /var/run/tor/control.
Under “Tor authentication settings” choose “No authentication, or cookie authentication”.
Click the “Test Connection to Tor” button.
If all goes well, you should see “Connected to the Tor controller”.